Sympathetic Nervous System Effects On Urinary Functions
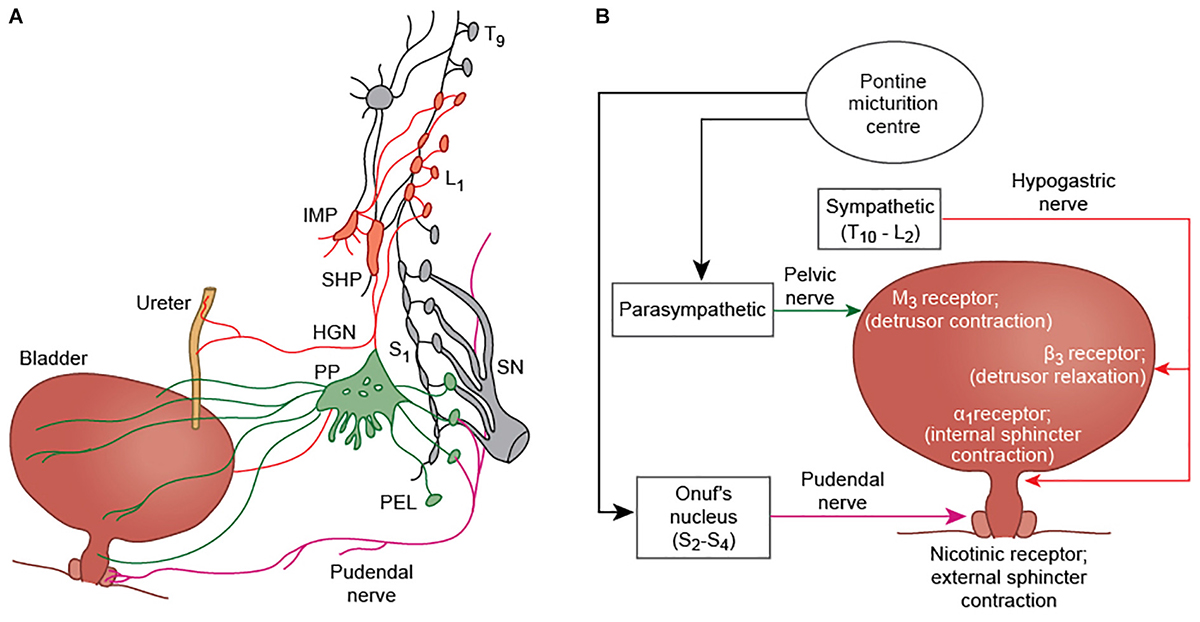
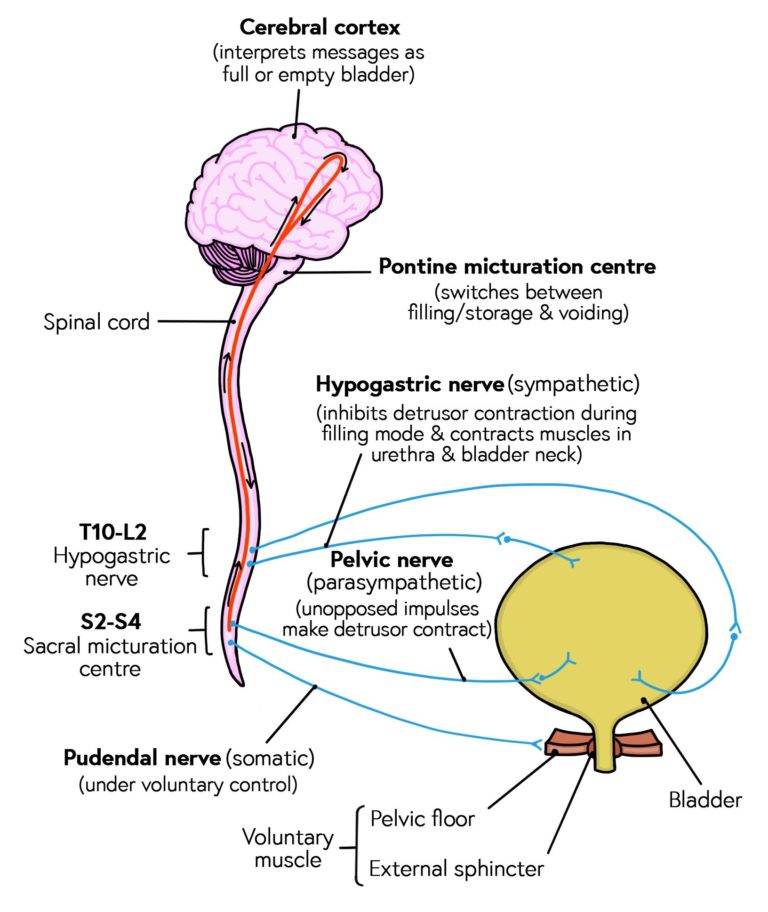
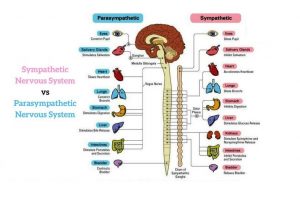
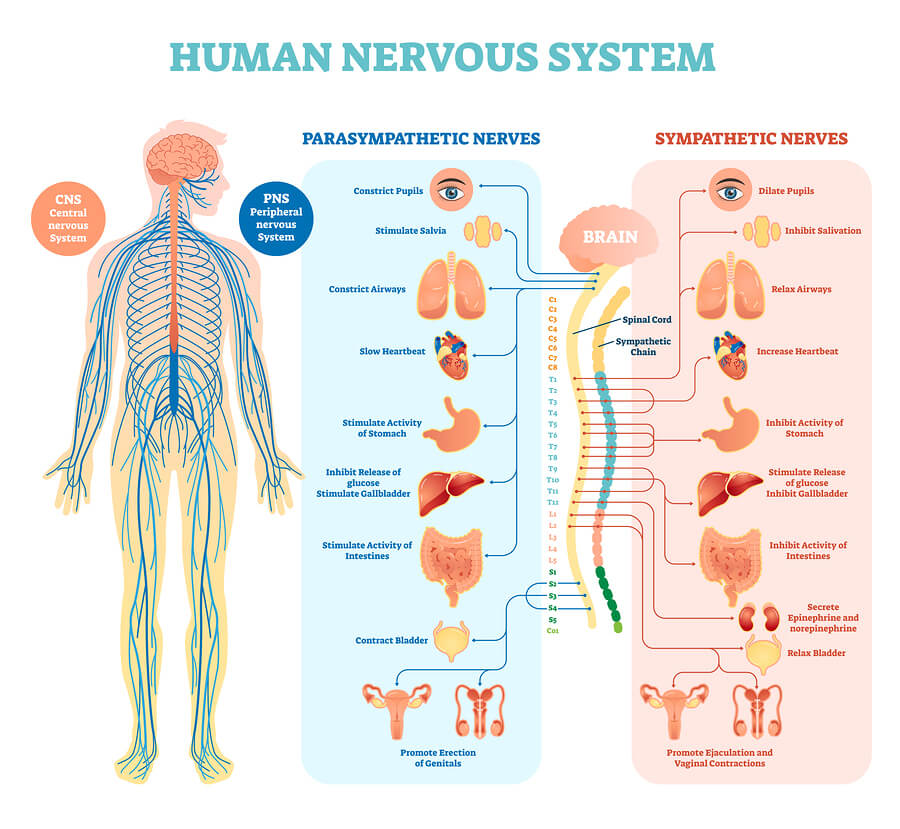
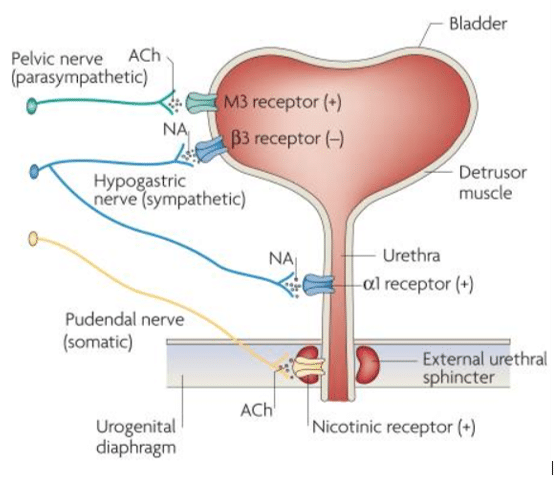
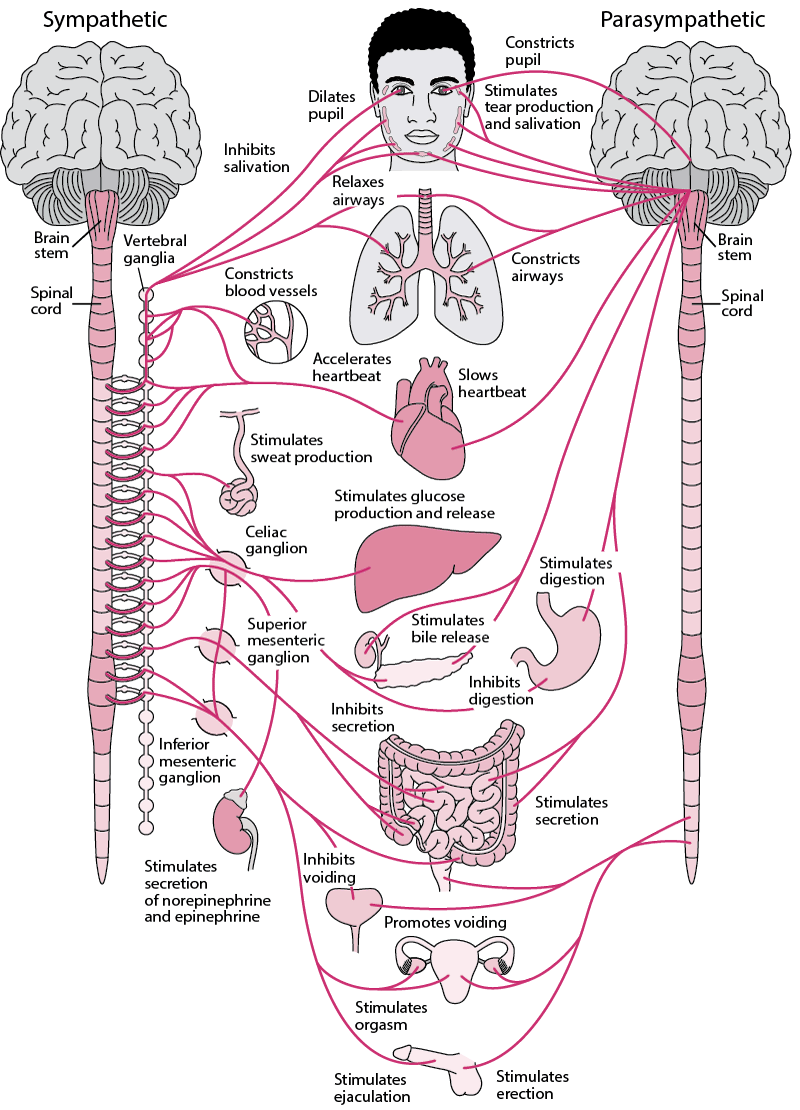
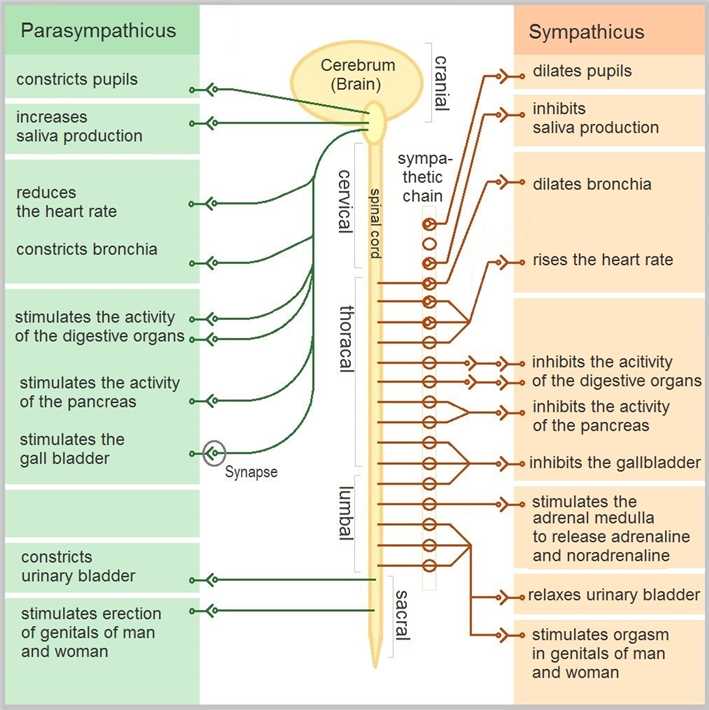
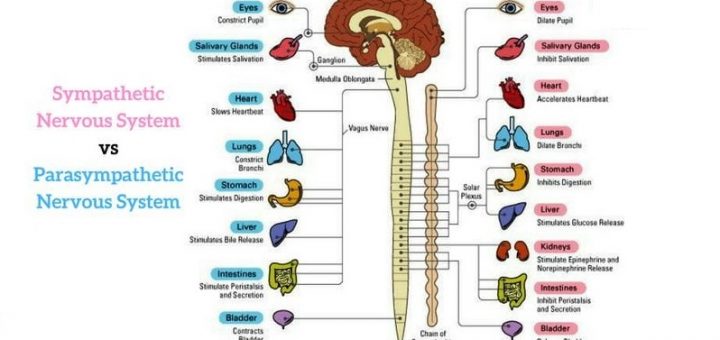
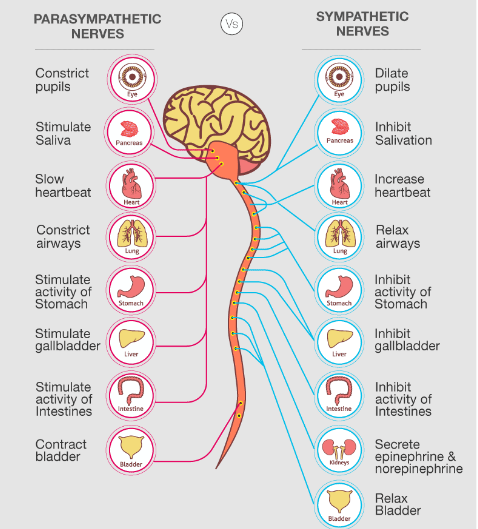
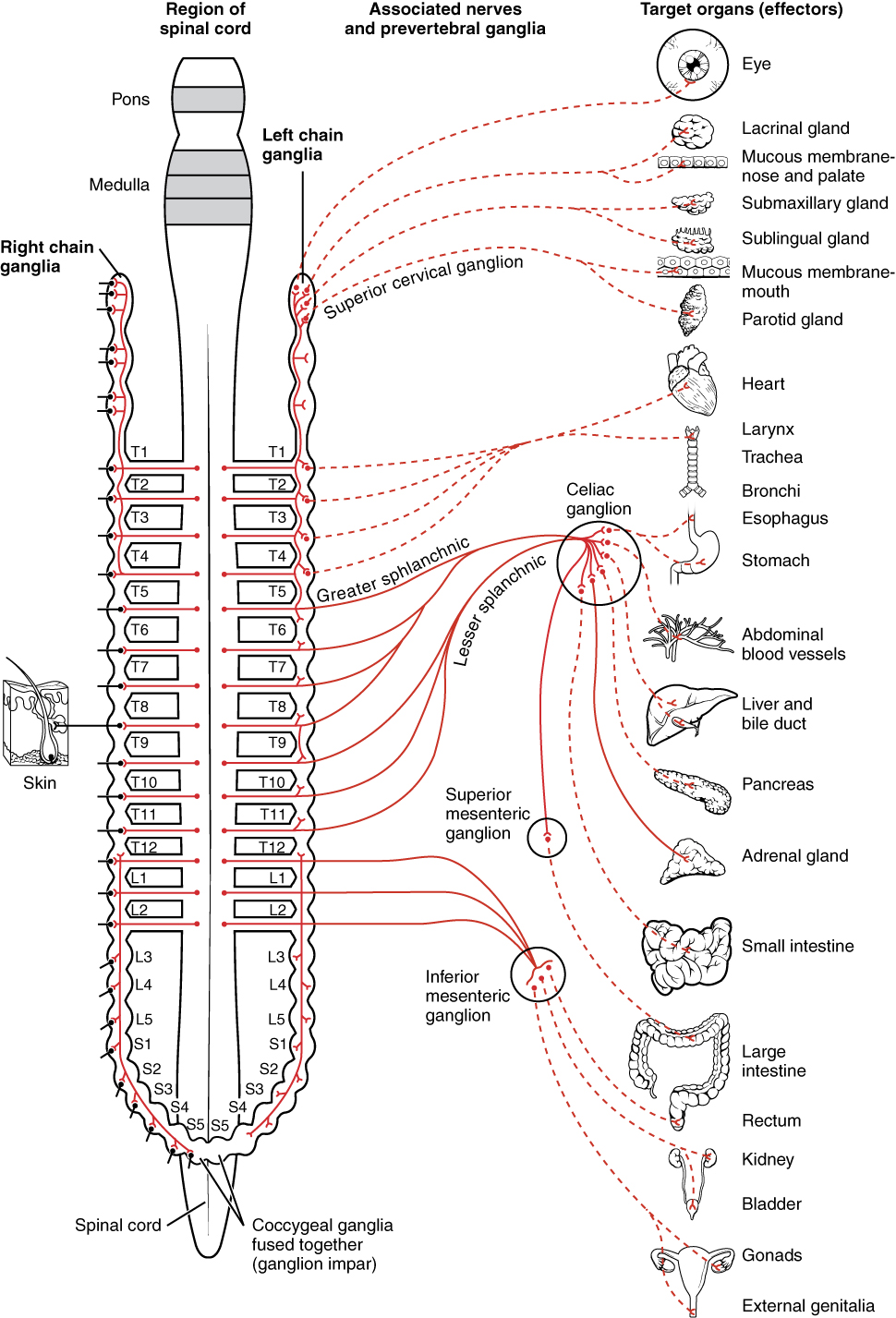
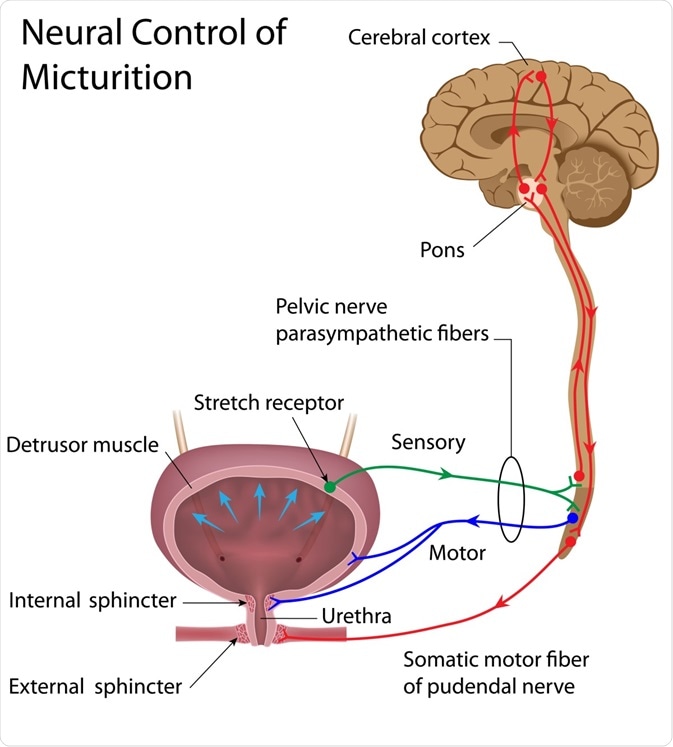
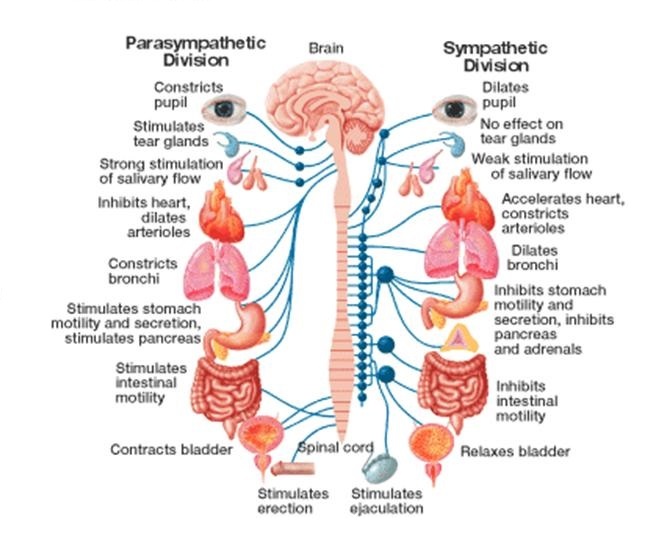
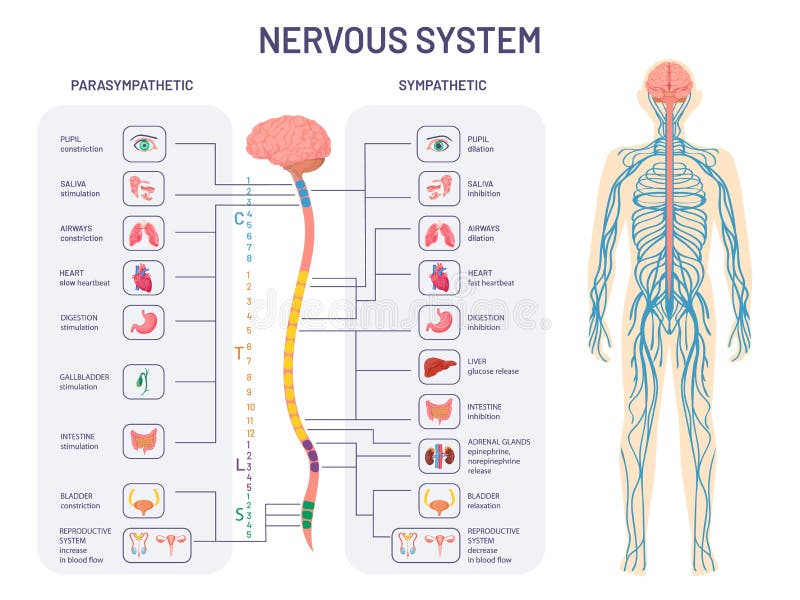
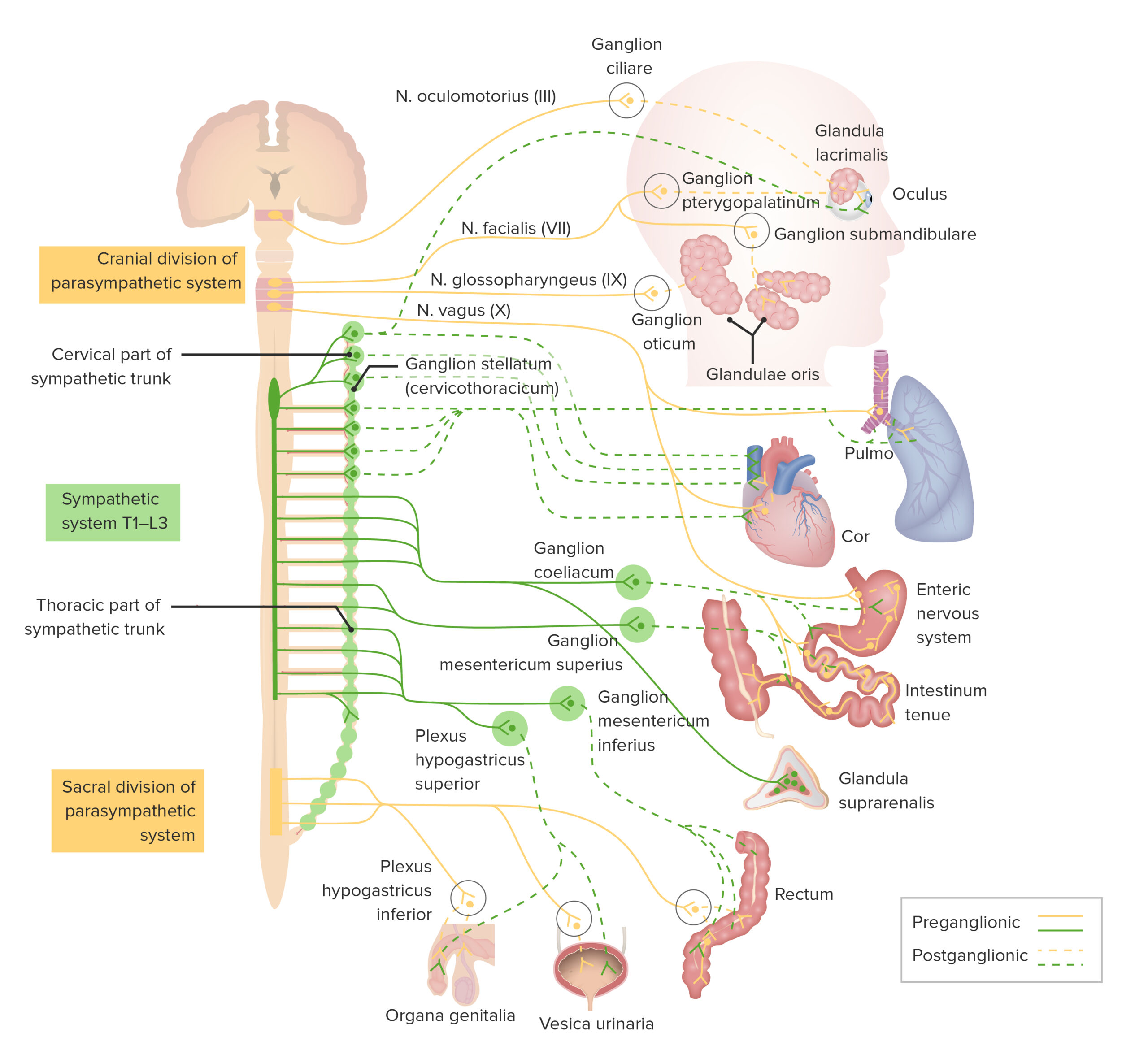
Sympathetic nervous system effects on urinary functions. The size of the post-ganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system is long. Instead the sympathetic nervous system SNS controls the bodys responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the fight or flight response. Pelvic parasympathetic nerves which arise at the sacral level of the spinal cord excite the bladder and relax the urethra.
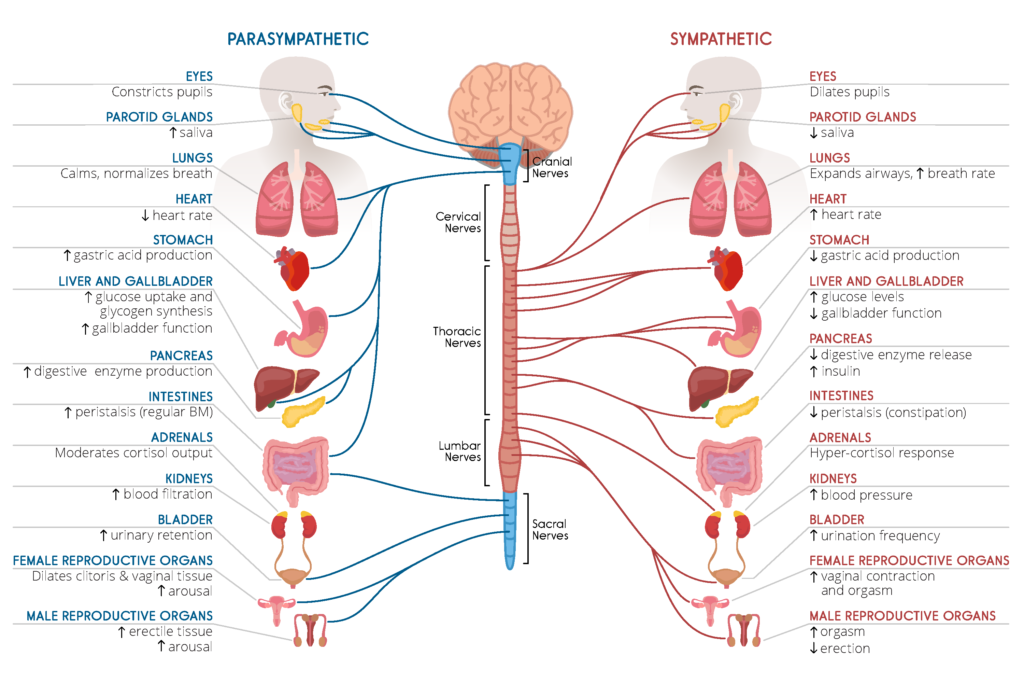
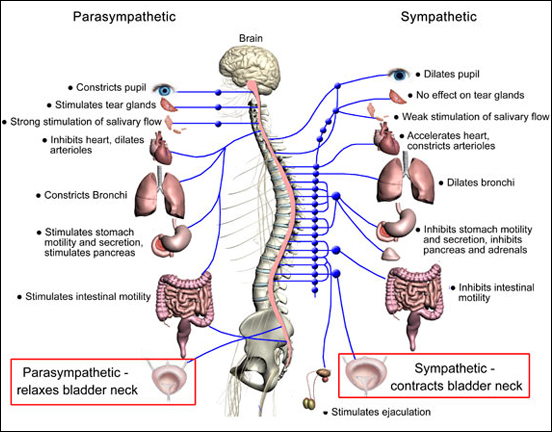
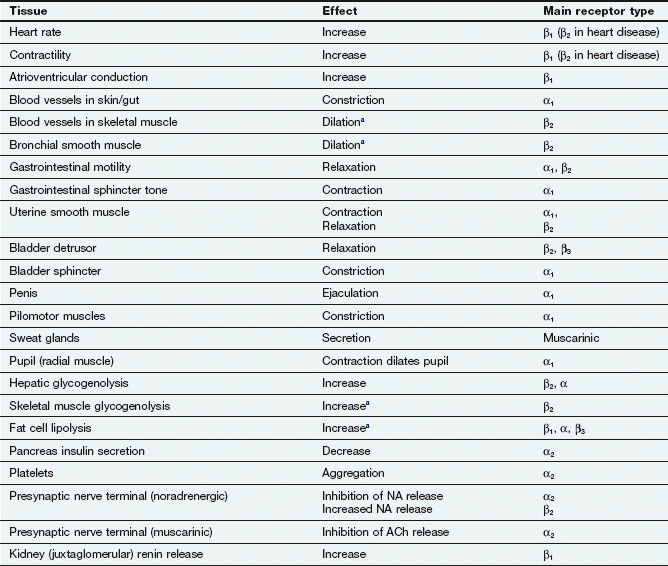
In the urinary bladder there is relaxation of the detrusor muscle and contraction of the urethral sphincter beta-22 to help stop urine output during sympathetic activation. Sympathetic nervous system decreases the urinary output and contracts the rectum. Mydriasis dilation of the pupil Skin.
Contracts urinary bladder Sympathetic Nervous System. The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for the fight or flight response during any potential danger. The exocrine and endocrine pancreas alpha-1 alpha-2 decreases both enzyme and insulin secretion.
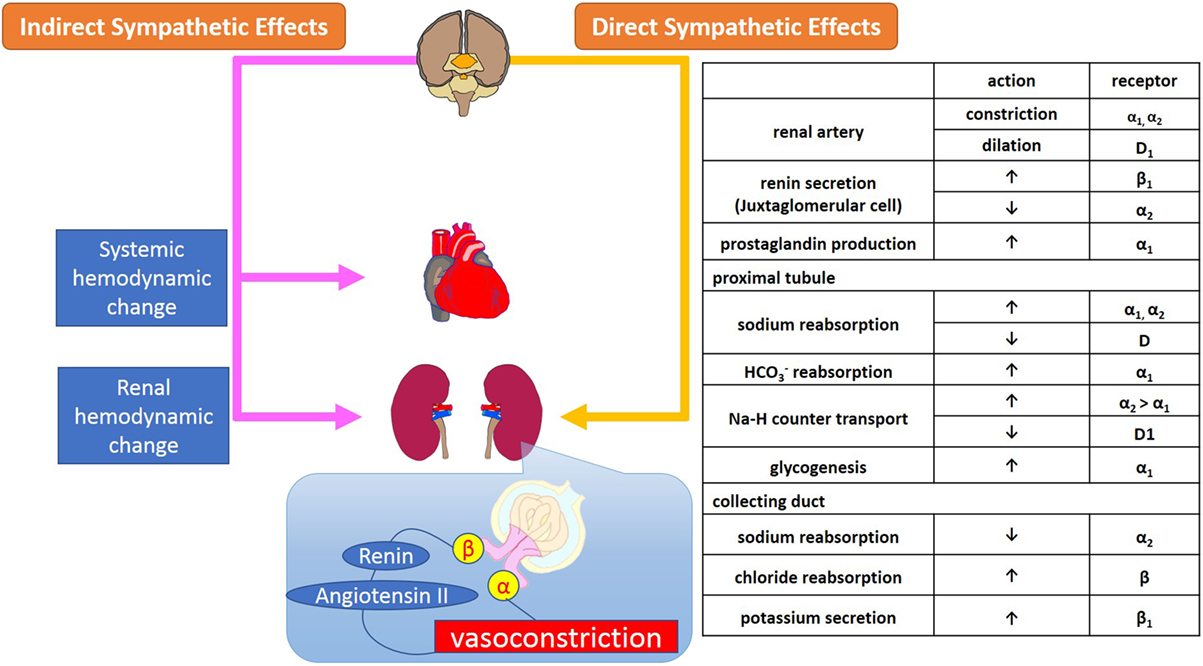
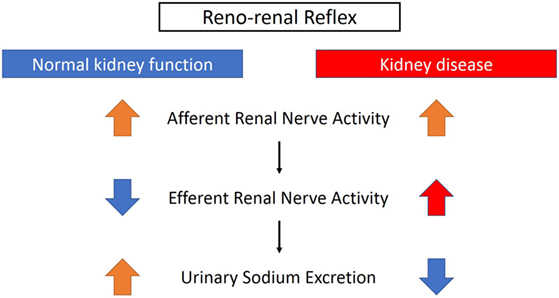
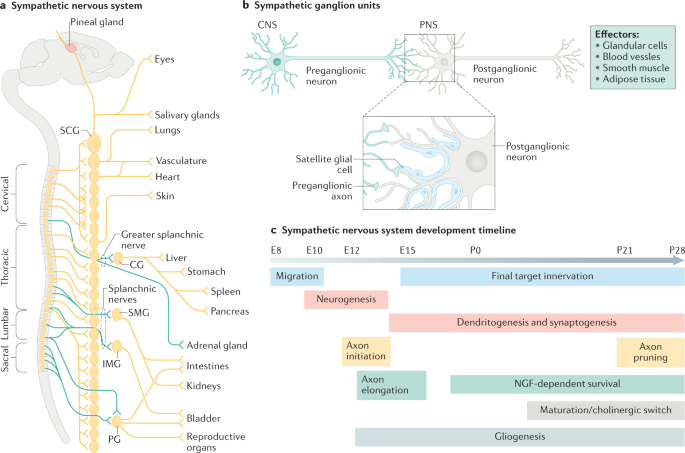
Lacrimal and salivary glands. Fibers from the SNS innervate tissues in almost every organ system providing at least some regulation of functions as diverse as pupil diameter gut motility and urinary system output and function. On the one hand the sympathetic nerve system affects renal function ie.
Renal hemodynamics renin secretion and tubular sodium transport. The secretion of watery saliva is stimulated by parasympathetic nerves whereas sympathetic nerves stimulate the constriction of blood. What does the sympathetic nervous system do to the bladder.
Inhibits activity of the digestive system like inhibition of peristalsis. The autonomic system has two divisions. Sympathetic stimulation contracts the meridionalfibers of the iris that dilate the pupil whereas parasym-pathetic stimulation contracts the circular muscle of theiris to constrict the pupil.
Increases heart rate and strength of contraction. They are 1 the pupillary opening and 2 the focus of the lens.
Contracts urinary bladder Sympathetic Nervous System.
What does the sympathetic nervous system do to the bladder. In contrast the parasympathetic nervous system controls bladder contractions and the passage of urine. The lower urinary tract is innervated by 3 sets of peripheral nerves. Increases heart rate and strength of contraction. What does the sympathetic nervous system do to the bladder. In the urinary bladder there is relaxation of the detrusor muscle and contraction of the urethral sphincter beta-22 to help stop urine output during sympathetic activation. Sympathetic nervous system generates an excitatory homeostatic effect. When the sympathetic nervous system is active it causes the bladder to increase its capacity without increasing detrusor resting pressure accommodation and stimulates the internal urinary sphincter to remain tightly closed. They are 1 the pupillary opening and 2 the focus of the lens.
Lacrimal and salivary glands. The primary function of the sympathetic system is to stimulate your fight-or-flight response which is a physiological reaction that happens in response to a perceived harmful event attack or threat to survival. Contracts smooth muscle vasoconstriction Lungs. Together they regulate the involuntary and reflexive functions of the human body. On the other hand the kidney is the source of activating afferent signals presumably via stimulation of chemoreceptors and baroreceptors. It consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Sympathetic stimulation contracts the meridionalfibers of the iris that dilate the pupil whereas parasym-pathetic stimulation contracts the circular muscle of theiris to constrict the pupil.

















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14062/gnEvUC2kgTFXvmrjP39Yw_Sympathetic_nervous_system.png)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13927/Parasympathetic_nervous_system.png)




:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14063/nervous-system-breakdown.png)

Post a Comment for "Sympathetic Nervous System Effects On Urinary Functions"